Understanding the Cognitive Basis of Procrastination, Emotional Dependency, and Impostor Syndrome
Understanding the Cognitive Basis of Procrastination, Emotional Dependency, and Impostor Syndrome
Blog Article
Why do some individuals struggle with emotional dependency or impostor syndrome? Science offers fascinating insights into these behaviors, helping us understand their roots and possible solutions.
In this article, we will examine the psychological mechanisms behind como se livrar da dependencia emocional procrastination, emotional dependency, and impostor syndrome. By understanding their underlying causes, you can take actionable steps toward self-improvement.
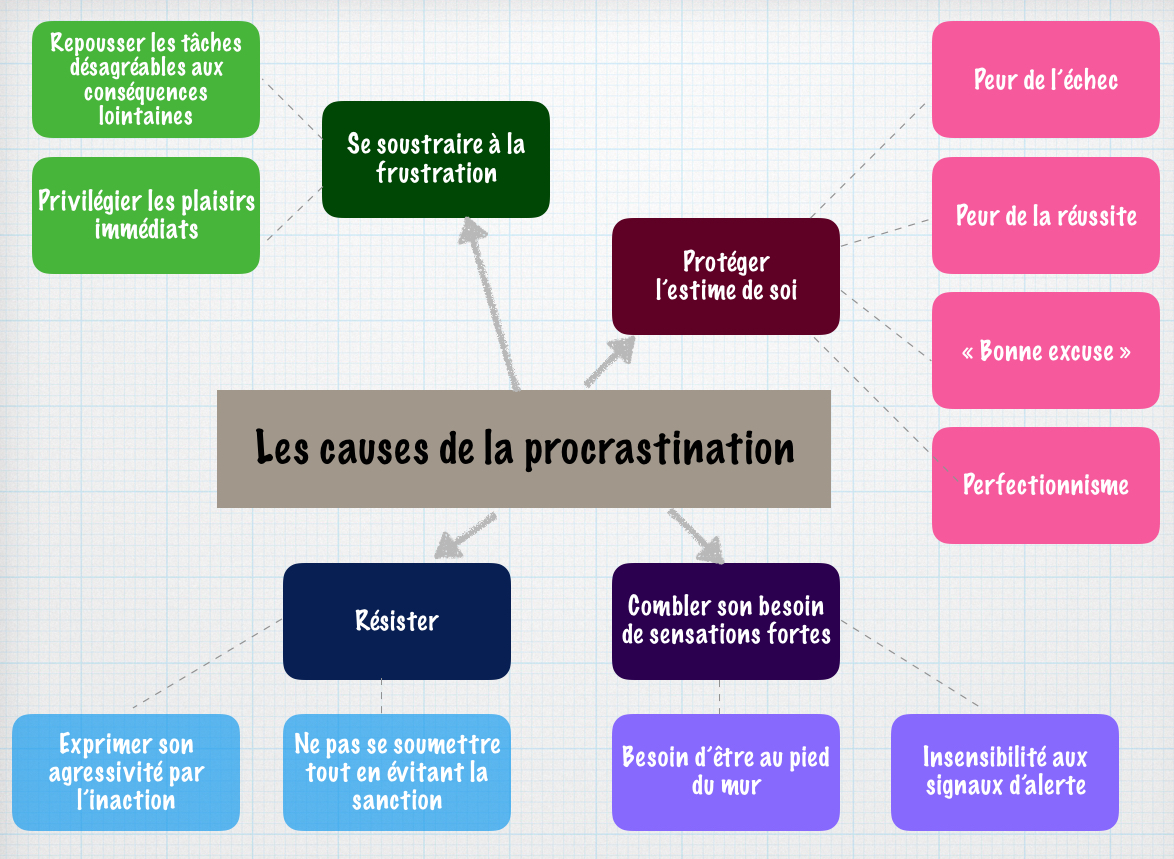
What is Procrastination?
Procrastination is often misunderstood as simple laziness; it’s a behavior rooted in brain functions. Studies in neuroscience show that the battle between the limbic system and the prefrontal cortex often leads to procrastination.

The limbic system, responsible for emotional responses, tends to dominate the logical decision-making center. This results in delaying tasks over long-term goals. Techniques like mindfulness and CBT can help rewire these patterns.
What is Emotional Dependency?
Emotional dependency is deeply tied to attachment theory. Studies suggest that childhood experiences and relational dynamics play a significant role in shaping dependency behaviors.
For example, people with insecure attachment styles may develop excessive reliance on others. To overcome emotional dependency involves building emotional self-reliance through practices like journaling, therapy, or mindfulness-based techniques.
The Cognitive Science of Impostor Syndrome
Impostor syndrome stems from biased mental patterns, such as unrealistic self-expectations. Psychological research indicate that individuals with impostor syndrome often engage in negative self-talk.
These distortions lead to a “fear of being found out” and difficulty in accepting success. Strategies like cognitive reframing and adopting self-compassion practices have proven effective.
Practical Solutions Backed by Science
Gaining a scientific perspective is the first step, but actionable strategies are necessary to create change. Here are key research-supported techniques:
- Procrastination: Use implementation intentions—specific plans that link a goal to a cue, such as “If it’s 9 AM, I will start writing my report.”
- Emotional Dependency: Practice self-differentiation, a technique where you focus on identifying your own needs separate from others’ expectations.
- Impostor Syndrome: Keep o que e dependencia emocional a success journal to document your accomplishments and review them regularly to challenge distorted self-perceptions.
These approaches are supported by empirical studies, making them effective pathways to improvement.
Conclusion: Science as a Guide to Personal Growth
These challenges are not insurmountable when approached with a scientific mindset. With evidence-based tools and self-awareness, you can overcome these barriers.
Awareness is the key to growth. Begin today by using the research-backed techniques shared in this article to build resilience and confidence.
Report this page